New: Flexible service plans for Myra WAF. Learn more!
Home>
Anycast
02
Advantages of Anycast
High Availability
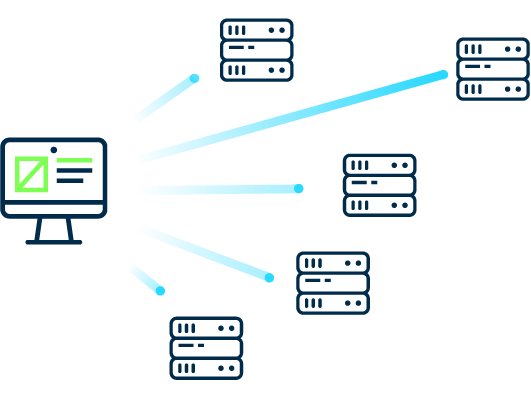
The failure of one or more servers can be compensated by anycast.
Load Distribution
Unnoticed by the sender, the load of the requests can be distributed among the different servers by always delivering the packets to the nearest server.
Shorter Access Times
The possible geographical proximity of the respective servers to the sender shortens the access time.
03
Alternative Routing Schemes
In addition to anycast there are other routing schemes that work differently.
Unicast
Unicast is the standard in data transmission where there is exactly one sender and one receiver. Unicast routing occurs, for example, when a user accesses a website hosted on a single server.
For the client there is no difference compared to unicast when using anycast, because the anycast servers can be reached via the same IP address. In most cases they also have a unicast address so that they can be addressed individually for administration purposes.
Multicast
In multicast, an endpoint sends data which is forwarded to the requesting devices via nodes. Multicast is used for IPTV transmissions, among others, to save bandwidth. As a result, not every device has to request the stream individually, but the stream is split and distributed onwards.
Broadcast
In broadcast, a single endpoint sends data to all endpoints in a broadcast domain. Among other things, television stations use this scheme for video and audio distribution.
Geocast
Geocast works in large part like multicast: An endpoint sends data to a variety of devices. However, geocast is limited to a specific geographical region. It is therefore mainly used for regional messages and services. The geographical area is determined by means of geo-routers and GPS data.
Cybersecurity Solutions by Myra

DDoS Protection
Myra DDoS Protection provides you with fully automatic protection against malicious requests and overload attacks. Even in the event of an imminent attack, your web applications stay available at all times.

Hyperscale WAF
The Myra Hyperscale WAF protects your web applications against malicious access and vulnerability exploits. Thanks to simple integration and configuration, it can be set up in no time at all.

CDN
First-class user experience thanks to fast page loading and minimal latency: With the Myra High Performance CDN, all static and dynamic content on your website is delivered with high performance.
Secure DNS
Myra Secure DNS offers you a reliable and powerful solution for securing your critical web applications. Manage your name resolution with ease and protect yourself against DNS hijacking.
Deep Bot Management
Say goodbye to malicious bots forever. Myra Deep Bot Management creates unique fingerprints for each bot and thus enables an optimal response to every request.
Certificate Management
No more problems with expired SSL/TLS certificates. Increase the security of your digital assets with Myra Certificate Management and encrypt all your domains automatically.
Want to learn more about our solutions, use cases and best practices for attack defense? In our download area you will find product sheets, fact sheets, white papers and case studies.
About the author
Stefan Bordel
Senior Editor
About the author
Stefan Bordel has been working as an editor and technical writer at Myra Security since 2020. In this role, he is responsible for creating and maintaining website content, reports, whitepapers, social media content and documentation. This role allows him to bring his extensive experience in IT journalism and technical knowledge to an innovative cyber security company. Stefan previously worked at Ebner Verlag (formerly Neue Mediengesellschaft Ulm) for 7 years and joined the online editorial team at com! professional after working for Telecom Handel. He gained his first journalistic experience during various internships, including at the IT website Chip Online. As a passionate Linux user, he follows the IT scene closely, both privately and professionally.