New: Flexible service plans for Myra WAF. Learn more!
Home>
CDN (Content Delivery Network)
03
Who Needs a CDN?
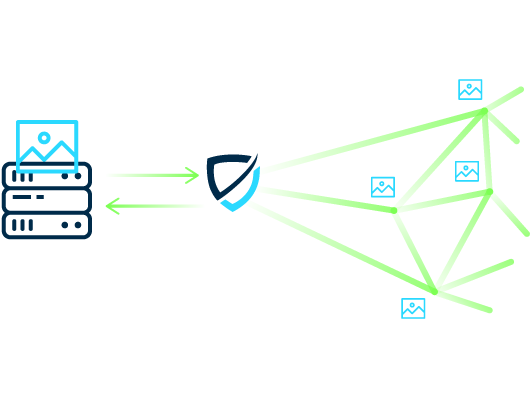
For many websites with high traffic volumes and international access, it makes sense to use a CDN service. Without a CDN, all traffic must be processed solely by the origin servers of the respective organization. These servers form a "single point of failure" when unexpected load peaks or hardware or software problems occur. In addition, long loading times can result if requests originate from geographically distant regions.
With the help of a high-performance content delivery network, however, webmasters can minimize loading times and latencies - even if an unexpectedly large number of requests occur in parallel. In addition, problems with the origin servers do not directly affect users, as website elements are still delivered via the CDN network. All of these factors improve the digital user experience and have a positive effect on search engine rankings.
Identify CDN Demand: Bandwidth, Latency and Reliability Requirements Are Crucial
These industries benefit most from the use of a CDN:

Public Sector
Public authorities use CDN services to protect themselves against outages in order to fulfill their duty to provide information even in exceptional situations.
Streaming Services
Streaming services for video and audio use content delivery networks for fast and reliable delivery of their digital content. The same applies to live streaming and gaming platforms.

E-Commerce
Online retailers improve their conversion rate with a CDN service thanks to faster loading times and shorter latencies.
Software Provider
Providers of software downloads and updates use CDNs to ensure the reliability of their services.
04. What Benefits Does a CDN Offer Companies?
Unternehmen profitieren bei Verwendung eines Content Delivery Networks von folgenden Vorteilen:

Failsafe Performance
CDNs handle unforeseen load peaks that would completely overload the Origin server.

Reduced Amounts of Data
CDNs compress web content. These smaller data volumes are sent much faster.
Optimized Media Streaming
Content delivery networks can distribute audio and video content with variable bit rates and dynamic resolution to ensure the best possible quality at all times.

Caching
CDN providers store web content on high-performance caching servers that respond to incoming requests from RAM memory. This enables higher performance to be achieved than with classic hard disks or SSD storage.
Lower Operating Costs
By reducing the load on the origin server through caching, expensive traffic can be avoided and bandwidth saved. The use of a CDN provider also enables cost-effective scaling.

Improved IT Security
Thanks to hardened server instances and optional protection functions, CDN providers can offer a high level of security for digital business processes.
07
Criteria for Selecting the Right CDN Provider
When looking for a suitable CDN provider, companies are faced with a wide range of options. In addition to traditional CDN providers that focus purely on the accelerated delivery of content, there are also specialized protection service providers on the market that offer comprehensive security solutions in addition to performance. The following criteria will help you choose the right CDN service:
Traffic Management
CDN providers handle global traffic management for their customers. Load balancing ensures the efficient load distribution of traffic. This can take place both at server level and at data center level in order to achieve optimum load distribution from the individual server instance to several data centers.
Network Security
When choosing a CDN provider, it is essential to ensure that it offers network security services and protects against distributed denial of service attacks (DDoS), for example. Furthermore, secure bot management is elementary.
Compliance
The use of CDN services requires encryption to be temporarily broken (SSL/TLS termination). Choosing a trustworthy and competent service provider for CDN services is therefore crucial to ensure confidentiality, integrity, authenticity and availability of data.
Geographical distribution of servers
A well-distributed network of servers worldwide is crucial for delivering content quickly to users around the world. The more edge servers there are in the regions where your target audience lives, the better the loading times and user experience will be.
Performance and speed
The performance of a CDN depends on latency, data throughput, and the ability to deliver content in real time. Providers should be able to offer fast caching and minimal time-to-first-byte (TTFB) to optimize website load times.
Integration and compatibility
Easy integration of the CDN with existing IT systems and platforms such as cloud services is a major advantage. Seamless integration helps minimize implementation effort and increase efficiency.
Which CDN providers are available?
Myra Security: Myra CDN offers a powerful combination of speed, security, and reliability. With its highly distributed edge architecture, Myra CDN ensures lightning-fast load times and optimal availability worldwide. In addition to classic CDN functions, Myra offers comprehensive protection against DDoS attacks and other security solutions that can be seamlessly integrated into existing IT systems. With a clear focus on critical infrastructures and regulatory requirements such as GDPR, Myra CDN is particularly suitable for companies that require the highest security standards and compliance – for example, as a Cloudflare alternative.
Cloudflare: Cloudflare is very popular for its easy integration and extensive security features. In addition to CDN services, Cloudflare offers protection against DDoS attacks, a web application firewall (WAF), and DNS services.
Amazon Cloudfront: Part of Amazon Web Services (AWS), CloudFront offers seamless integration with other AWS services. It is scalable and is often used by companies that already rely on AWS.
Akamai Technologies: Akamai is one of the largest and best-known CDN providers worldwide. They offer a wide range of security and performance solutions and are particularly strong in the areas of DDoS defense and web security.
Fastly: Fastly is known for its fast and flexible edge computing solutions. They have a strong presence in the streaming and media industry and offer comprehensive security and optimization features.
Frequently Asked Questions About CDN
A content delivery network (CDN) is a network of locally distributed servers that are connected to each other via the internet. This reduces the distance between the user and the content to be delivered and a website can be delivered faster, e.g. with the help of caching.
A CDN (sometimes also called a CDN network) enables websites around the world to load quickly. This is achieved by caching and delivering website content on several connected servers in different geographical locations.
The costs for CDN services vary considerably depending on the scope of services and support requirements. Many basic CDN services are extremely inexpensive - some are even free. However, such services are less suitable for use in companies because there are severe restrictions on bandwidth, capacity, scope of protection and, above all, support. These services are only included in the CDN providers' higher-priced plans. However, these services are still much cheaper than setting up a comparable CDN service in-house.
CDN servers are stationed at strategically important locations such as globally distributed internet nodes in order to create a network that is as performant and fail-safe as possible. Static website content, including CSS and JavaScript files as well as images, is stored on these servers. When a user accesses the website in question, the request does not have to travel across several continents to reach a specific server. Instead, the CDN uses the server closest to the user to establish the connection. This speeds up data transfer and the website loads faster.
When choosing a provider, companies that attach great importance to data protection often ask themselves which CDN providers Germany has to offer. In addition to globally active CDN providers and cloud hyperscalers, Germany is predominantly home to highly specialized providers in the CDN sector that offer both performance and protection services for companies. When choosing a suitable CDN provider, organizations should primarily focus on the provider's industry expertise and certification level. Standards such as ISO 27001 based on BSI Grundschutz, BSI-C5 Type 2 or KRITIS qualification in accordance with Section 3 of the BSI Act are indicators of a CDN provider with a high level of security and data protection expertise.
Would you like to find out more about our solutions, application examples and best practices for attack defense? In our download area you will find product sheets, fact sheets, white papers and case studies.
About the author
Stefan Bordel
Senior Editor
About the author
Stefan Bordel has been working as an editor and technical writer at Myra Security since 2020. In this role, he is responsible for creating and maintaining website content, reports, whitepapers, social media content and documentation. This role allows him to bring his extensive experience in IT journalism and technical knowledge to an innovative cyber security company. Stefan previously worked at Ebner Verlag (formerly Neue Mediengesellschaft Ulm) for 7 years and joined the online editorial team at com! professional after working for Telecom Handel. He gained his first journalistic experience during various internships, including at the IT website Chip Online. As a passionate Linux user, he follows the IT scene closely, both privately and professionally.