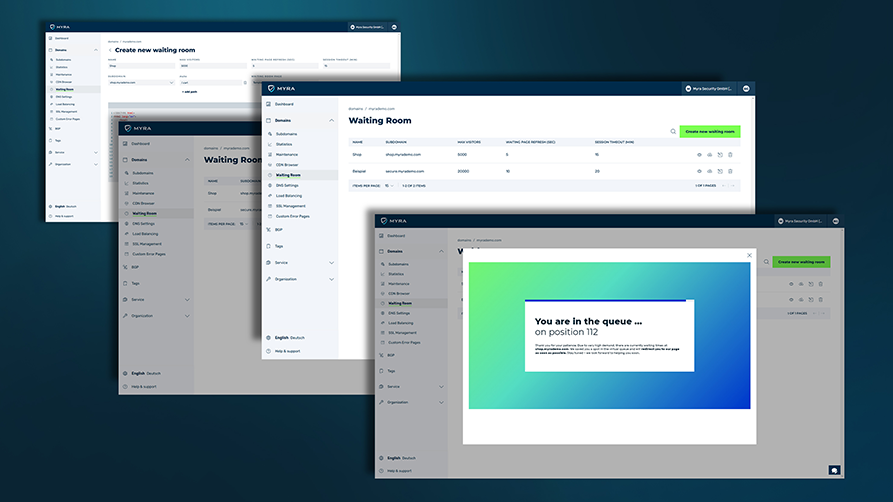
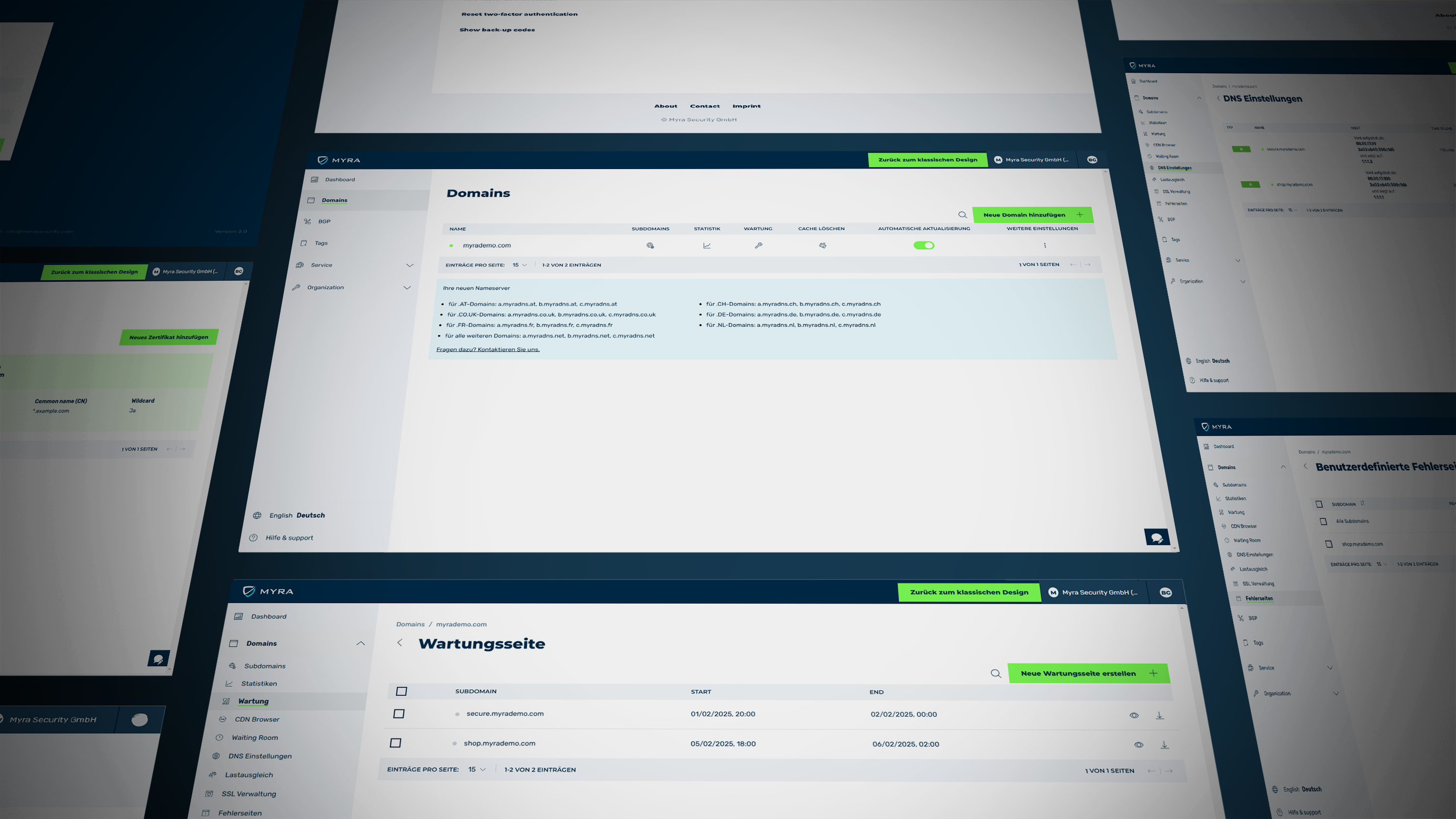
New: Flexible service plans for Myra WAF. Learn more!
News & Insights
Security Insights
03 July 2025
Our data is a suitcase – but who has the key?
Like TSA-certified suitcases, SSL/TLS-encrypted data can also be temporarily opened with a master key. But what if providers from the US hold the key? An article about digital sovereignty and the question of who we should trust in uncertain times.

Security Insights
30 June 2025
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – June 2025
Cyberattacks on healthcare, government agencies, and communications services highlight the growing vulnerability of critical infrastructure and the urgency of digital sovereignty. The latest BKA situation report and new EU initiatives underscore that security and resilience must be a priority now.

Security Insights
01 June 2025
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – May 2025
Wake-up call for greater digital sovereignty: As the global cyber threat landscape continues to escalate due to geopolitical tensions, experts are calling for sovereign solutions in the digital supply chain to ensure availability and reduce dependencies.

Myra News
20 May 2025
Bavarian Cybersecurity for Europe's Data
We had the opportunity to discuss the role of security-as-a-service “made in Germany” with Minister of State Dr. Florian Herrmann. The clear message: Bavaria, Germany, and Europe need strong local providers and a trustworthy IT infrastructure to secure digital sovereignty.
Security Insights
13 May 2025
Myra protects German banks from massive wave of DDoS attacks
Following attacks on German city portals, cybercriminals targeted banks and financial service providers with DDoS attacks. Myra defended affected customers. Even complex attack vectors such as Slowloris were detected early and repelled.

Security Insights
05 May 2025
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – April 2025
A massive wave of DDoS attacks on German authorities and companies at the end of April once again underscored the growing importance of proactive cyber defense. In the Myra Minds Podcast, Prof. Dr. Dennis-Kenji Kipker explains the importance of digital sovereignty in IT security against the backdrop of compliance risks. Meanwhile, investigative authorities have achieved significant successes in the fight against cybercrime by shutting down central malware platforms.

Myra News
22 April 2025
"Myra Minds" – the New Podcast for Cyber Resilience and Digital Responsibility
In our podcast, we discuss the most important topics relating to IT security, compliance, data protection, and cyber resilience. Host Cristof Klaus, Director of Global Network Defense at Myra, talks to experts from the worlds of IT, business, and politics about current challenges, opportunities, and trends.
Security Insights
31 March 2025
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – March 2025
Confidence in the USA as a reliable partner is increasingly crumbling. European trade associations and data protection authorities are equally warning of the risks that a sudden discontinuation of the EU-US data privacy framework (DPF) could entail.

Security Insights
03 February 2025
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – January 2025
The digital world is facing major challenges: The Myra Cybersecurity Report 2025 paints a dynamic picture of the current threat situation, while delays in NIS 2 implementation and political developments in the US continue to jeopardize cybersecurity and data protection.
Security Insights
04 December 2024
Cyberrisks to the German Federal Election: Four Key Questions About Security
In the context of the 2025 federal election, political parties, election authorities and other stakeholders are at risk of targeted attacks. Christof Klaus, Director of Global Network Defense at Myra Security, explains the potential cyberthreats and best practices for effective threat prevention.

Security Insights
28 November 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – November 2024
While the number of cyber attacks in Germany is increasing dramatically, national and international investigative authorities are successfully taking down cybercriminal networks. But can these successes contain the growing digital threat that is unfolding in times of political upheaval?

Security Insights
31 October 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – October 2024
As the cyber security situation continues to worsen in the final quarter, more and more German companies are investing in comprehensive protective measures. At the same time, it is becoming clear once again that cyber attacks pose an existential threat to organizations.

Security Insights
17 October 2024
Escalating DDoS Threat Situation Calls for Strategic Responses
The cybersecurity situation has dramatically worsened over the past few months. In the Q3 2024 update, you can learn more about the current developments based on data from the Myra Security Operations Center. Particularly, the increase in DDoS attacks on public institutions highlights the urgency of holistic protection measures.
Security Insights
02 September 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – August 2024
The threat situation for the German economy is intensifying massively, with increasing damage caused by cybercrime. Among other things, this is due to the significant increase in malicious data streams in the form of DDoS attacks, attacks on vulnerabilities in online applications and bot-based attacks.

Security Insights
01 August 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – July 2024
The Crowdstrike incident has highlighted the importance of redundant processes in IT infrastructure to minimise downtime and data loss. Meanwhile, the implementation of NIS-2 in Germany is progressing, but its timely implementation by October 2024 is still questionable.
Myra News
23 July 2024
Dennis-Kenji Kipker joins the Myra Advisory Board
Myra Security is expanding its advisory board with the renowned IT law expert Prof. Dr. Dennis-Kenji Kipker, Research Director of the cyberintelligence.institute and Professor of IT Security Law at the University of Bremen. Kipker will advise Myra in the areas of cybersecurity law, corporate strategy and digital resilience.

Security Insights
01 July 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – June 2024
Inadequately patched vulnerabilities are a frequent gateway for cyber attacks. In June, attackers used vulnerable security gateways to penetrate the systems of the CDU and KRITIS operators. Meanwhile, security authorities are increasingly concerned about the influence of artificial intelligence on cybercrime.

Security Insights
02 May 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – April 2024
Zero-day exploits on the rise: The threat of targeted attacks on newly discovered security vulnerabilities for which no patches yet exist is increasing rapidly. Two trends in particular are responsible for the intensified threat situation.
Myra News
08 April 2024
Palo Alto Networks CSO joins Myra Security Advisory Board
Myra Security has appointed Sergej Epp to its newly formed Advisory Board. Epp is Chief Security Officer (CSO) of the cyber security provider Palo Alto Networks. In his strategic role on the Advisory Board, he advises Myra on its further growth.

Security Insights
02 April 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – March 2024
The public sector is more at risk from cybercrime than ever before. A wave of massive DDoS attacks hit public organizations in France in March. Overall, the threat situation is becoming more critical due to overload attacks, as a recent IT security survey shows.

Security Insights
12 March 2024
Massive DDoS attack on French authorities
Cyber criminals have hit large parts of the French administration with a massive wave of DDoS attacks. Myra security expert Rebecca Roche explains in an interview how administrative authorities can protect themselves against such attacks and what to do in an emergency.
Security Insights
01 March 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – February 2024
Europe has become the epicenter of cybercrime. In Germany, spending on IT security has exceeded the €10 billion mark for the first time. Despite successful raids by investigating authorities, cyber groups are quickly reappearing on the scene.

Security Insights
01 February 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – January 2024
According to the latest Allianz Risk Barometer, cyber incidents are the top business risk for companies in Germany and worldwide. The German financial supervisory authority BaFin shares this view: it classifies cyberattacks as one of the main risks for the financial sector.

Security Insights
03 January 2024
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – December 2023
According to the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA), DDoS attacks continue to pose a serious threat. The most affected sector is the government administration sector. More than half of all attacks caused total disruption in the target.

Security Insights
01 December 2023
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – October 2023
The new Rapid Request attack method threatens countless web servers worldwide via a gap in the HTTP/2 network protocol. Meanwhile, cities and local authorities are increasingly being targeted by cyber criminals. DDoS attacks and encryption Trojans are paralyzing central specialist procedures and cutting off communication channels to citizens.

Security Insights
02 October 2023
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – September 2023
According to Germany's digital association Bitkom, data theft, espionage and sabotage cause annual damage of 206 billion euros to the German economy. In September, in addition to extortion attacks, there were again numerous politically motivated DDoS attacks.

Security Insights
01 September 2023
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – August 2023
Artificial intelligence and criminal energy: cybercriminals are increasingly abusing the power of intelligent systems for their attacks. Research teams are therefore focusing their attention on the question of which attack scenarios the new technologies make possible.

Security Insights
29 August 2023
Cyber Resilience Act makes security by design a must
The CRA defines specific cybersecurity requirements and support specifications for digital products in Europe for the first time. In this way, the EU Commission aims to strengthen the protection of consumers and companies alike.

Security Insights
03 August 2023
Web Application Security Report H1 2023
Defcon DDoS: Authorities on alert – In the first half of 2023, Myra's Security Operations Center (SOC) saw a 186 percent year-over-year increase in malicious requests. Most attacks targeted public sector organizations. Read this and more in our H1 2023 semi-annual report.

Security Insights
01 August 2023
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – July 2023
The BSI has new leadership and is to be given new powers to oversee the regulation of NIS-2-regulated companies. Meanwhile, a new data protection agreement between the EU and the U.S. enters into force, which has been sharply criticized from the start.

Security Insights
23 June 2023
How to avoid downtime: identify and fix the 9 most common causes
Optimal availability and performance are the basic prerequisites for successful websites. In contrast, online service outages cause massive damage. In the Myra Fact Sheet on Downtime Minimization, IT managers find out how to protect their company from such damage.
Security Insights
24 May 2023
Success Story: Minimizing Downtime for the Federal Ministry of Health
The Federal Ministry of Health was struggling with website downtime due to unexpected traffic spikes and DDoS attacks. Thanks to Myra's GDPR-compliant protection and performance solutions, the ministry was able to minimize the downtime.

Security Insights
04 May 2023
Threat Assessment: Assess your attack risk now and identify appropriate protection solutions
Assess your individual threat situation and your current level of protection to specifically optimize your application and network security - quickly and easily with the Myra Threat Assessment Card.

Security Insights
27 April 2023
New DDoS attack vector: SLP vulnerability enables amplification attacks with factor 2,200
It should not be long before cybercriminals abuse one of the more than 50,000 vulnerable SLP instances visible on the Internet for volumetric attacks. Myra customers can rest easy, however.

Security Insights
31 March 2023
Trending Topics Cybersecurity – March 2023
Public authorities and the healthcare sector are frequent targets for cyber criminals. These sectors are particularly susceptible to blackmail methods, as extremely sensitive information is processed there. The attackers' unscrupulousness knows no bounds.

Security Insights
03 June 2022
Attackers exploit zero-day vulnerability in Atlassian Confluence for remote code execution
Attackers are using a zero-day vulnerability in Confluence Server and Data Center to deliver malicious code to vulnerable systems - threatening massive damage. Learn how Myra protects against the new threat here.

Security Insights
18 March 2022
Fend off DDoS extortion: Success Story with mailbox.org
The mailbox.org email service was targeted by DDoS extortionists last fall. With the help of Myra Security, the operator Heinlein Hosting was able to secure the availability of the service without paying protection money.

Myra News
23 February 2022
Barbarians, knights & cybercriminals - Myra promotes more IT security with creative appeal
Myra's IT awareness campaign launches on February 23, 2022, and the centerpiece of the campaign is a nearly two-minute film, "The History of Attacks," in which two heroes, Brian and Pete, embark on a perilous journey through time.

Security Insights
24 January 2022
Log4J vulnerability: internet on red alert
The critical “Log4Shell” vulnerability in the Java Log4J library enables attackers to inject malicious code on web servers and inflict massive damage. Find out everything you need to know about the vulnerability and how you can protect yourself.

Security Insights
19 November 2021
Operational resilience: BaFin puts even greater focus on cybersecurity
BaFin has set itself the goal of strengthening the operational resilience of the financial industry. An important part of this is the digital safeguarding of banks, insurance companies, and affiliated service providers.

Security Insights
27 October 2021
Regulators take action against unauthorized use of U.S. cloud service providers
In an interview, KPMG legal expert Sebastian Hoegl reveals how Europeancompanies can best respond when they get a letter from the data protection authority or have concerns about whether they are violating data protection provisions by using U.S. cloud service providers.

Myra News
21 October 2021
ISO 27001 based on IT-Grundschutz (IT baseline protection): Myra Security renews strict BSI certification
BSI-approved: With re-certification according to ISO 27001 based on IT-Grundschutz (IT baseline protection), Myra has once again demonstrated its successful implementation of demanding measures for the protection of corporate IT.

Security Insights
24 August 2021
223 billion euros in damage caused by cyber attacks – why the number of unreported cases is much higher
When critical infrastructure is attacked, the actual damage is far greater. That is why the protection of critical infrastructure is fundamental to the well-being of us all.

Security Insights
20 August 2021
BaFin revises MaRisk and BAIT: Higher compliance requirements for banks
In light of advancing digitalization, cybersecurity is becoming an even greater focus of supervisory attention. Institutions must prepare for new or more specific regulations related to outsourcing, contingency management, and effectiveness controls, for example.

Events
12 August 2021
#WTI21: Cybersecurity is the new Made in Germany
At the German Economic Council’s Day of Innovations, the head of the BSI, Arne Schönbohm, spoke with Myra CEO Paul Kaffsack about cybersecurity as a driver of innovation for Germany. Where do we stand and what do we need for global success?

Security Insights
19 May 2021
IT security creates a foundation of trust for e-health solutions
In the healthcare sector, digital solutions are increasingly being used in administration, diagnostics, and treatment. Security and data protection are given top priority in order to promote social acceptance of e-health.

Security Insights
03 September 2020
BaFin demands higher hurdles for IT outsourcing
Raimund Röseler, BaFin Executive Director for Banking Supervision, is in favor of IT outsourcing to qualified service providers. However, he is calling for the right of direct control over the service providers. Banks must choose their IT partners with care.

Security Insights
15 July 2020
Digitalization in healthcare in demand as never before
Digitalization in healthcare in demand as never before
International studies show that patients are increasingly demanding digital treatment methods such as telemedicine, health apps or AI-supported diagnosis programs. However, IT security, data protection and compliance are the basis for successful digitalization in the healthcare sector.